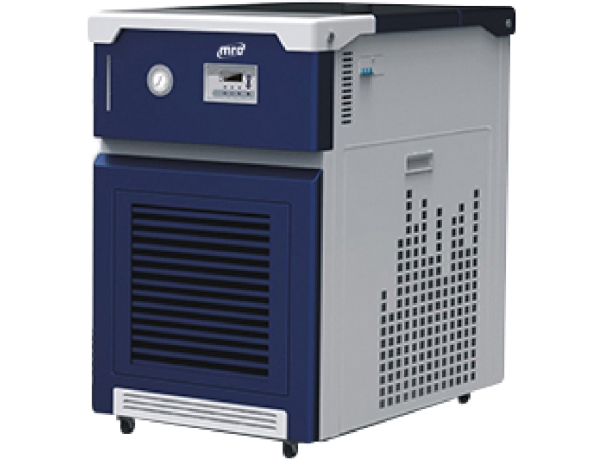
Chillers are machines that remove heat from a liquid via a vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycle. This liquid can then be circulated through a heat exchanger to cool air or equipment as required. As a necessary byproduct, refrigeration creates waste heat that must be exhausted to ambient or, for greater efficiency, recovered for heating purposes. Concerns in the design and selection of Laboratory chillers include performance, efficiency, maintenance, and product life cycle environmental impact. You can see our products: Recirculating chillers, recirculating coolers, Water Cooler. The main purpose of a chiller is to remove heat from one area and pass it to sources like ambient air or water.
Important specifications to consider when searching for industrial chillers include:
Process pump selection Industrial chiller selection
Process flow Total life cycle cost
Process pressure Power source
Pump material Chiller IP rating
Elastomer & mechanical shaft seal material Chiller IP rating
Motor voltage Chiller cooling capacity
Motor electrical class Evaporator capacity
Motor IP rating and pump rating Evaporator material
If the cold water temperature is lower than the Evaporator type
−5°C, then a special pump needs to be used Condenser material
to be able to pump the high concentrations of Condenser capacity
ethylene glycol Ambient temperature
Internal water tank size Motor fan type
Full load current noise level
**Control panel features that should be Internal piping materials
considered when selecting between industrial Number of compressors
chillers include: the local control panel, Type of compressor
remote control panel, fault indicators, Number of fridge circuits
temperature indicators, & pressure indicators. Coolant requirements
Additional features include emergency Fluid discharge temperature
alarms, hot gas bypass, city water COP (the ratio between the cooling capacity
switch over, and casters in RT to the energy consumed by the whole chiller in KW). For medium, to large chillers, this should range from 3.5 to 7.0, with
higher values meaning higher efficiency. Chiller efficiency is often specified in kilowatts per refrigeration ton(kW/RT).
Choosing a laboratory and industrial chiller
The choice of chiller is made according to the requirement of the hot system, to what temperature it is necessary to lower it, and what the cooling power and flow are needed to flip the heat. The choice of the chiller is made according to the cooling power, cooling temperature, flow and pressure
